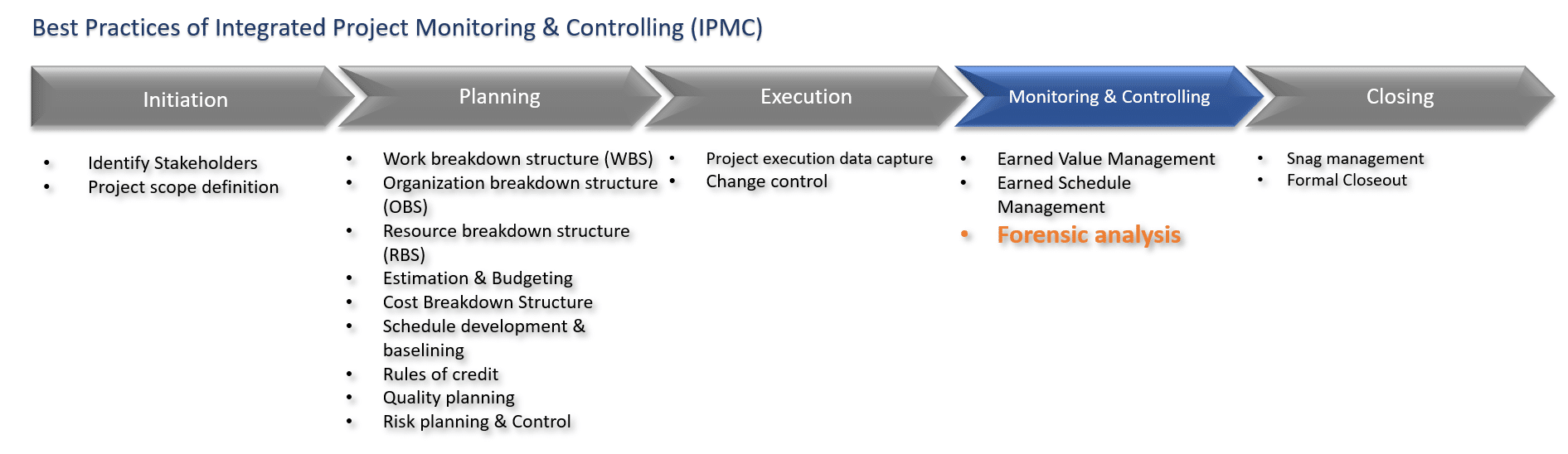
Forensic analysis
Forensic analysis
Lesson Objective
To introduce the participants to forensic analysis
Effort required – 15 minutes
Lesson Introduction
In simple terms, forensic analysis consists of examining:
- what happened on a project?
- did it deviate from the original plan?
- who was responsible for the delay?
- what effect did the delay have on project completion?
- was any remedy proposed to bring the project back on track and lastly;
- whether there is sufficient information to contest a claim in court
Forensic delay analysis, like many other technical fields, is both a science and an art. As such, it relies upon professional judgment and expert opinion and usually requires many subjective decisions.
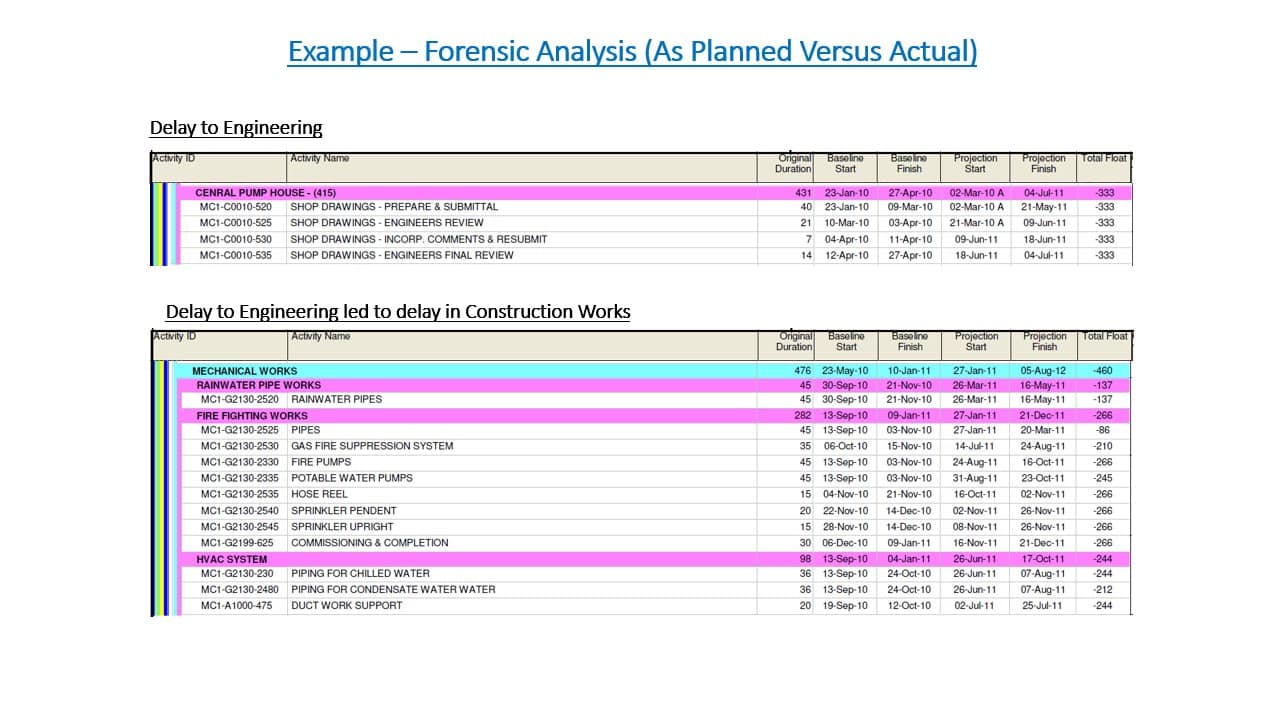
The first important decision in forensic analysis is to choose which Delay Analysis Technique (DAT) is to be applied.
The next step is to identify:
Cause – identify the affected activities, and
Effect – measure/ quantify the delay
Sources of project disputes
Most project disputes can be categorized into two main categories:
i. Time impact – delays to completion of project milestones;
ii. cost impact – additional expenses incurred that were not envisaged at the time of tender;
Delay Analysis Methodologies
Delay analysis methodologies fall into two distinct categories:
i. Prospective – which seek to establish the ‘likely’ delay of an event to the completion of the works.
ii. Retrospective – which seek to establish the causes of ‘actual’ delay to the completion of the works.
The method employed may be:
a) Modelled – Adding, modifying or removing activities from a network to identify the potential effect of a change; or
b) Observational – Analysis by comparison of information in order to extract details of changes and to identify or discount likely reasons for changes.
Delay Analysis Techniques – Brief overview of some commonly used techniques
There are many different delay analysis techniques used within the industry. The selection depends on the needs of the analysis, in conjunction with due consideration of the Contract, the nature of the events in dispute between the parties, the contemporaneous information available, and the quality & extent of program information available.
There are four different main types of delay analysis methods that are commonly used (and further variants of these types). These are:
I. Impacted As-Planned method – A modelled approach based on the addition of delay events to the baseline program to establish the impact on the original planned completion date and hence entitlement. This can be applied prospectively or retrospectively.
II. Time Impact Analysis method – A modelled approach that can be applied prospectively or retrospectively. The delays are developed as activities or groups of activities (fragnets) then added sequentially. This allows the impact of an event to be modelled and noted before the next is added.
III. As-Planned v As-Built method – An observational approach based on comparison between a baseline program and an as-built program to identify and then investigate causes of delays. This can be applied prospectively or retrospectively.
IV. Collapsed As-Built method – A modelled approach where the final as-built program is modified to identify and remove all the delay events under consideration. The corresponding reduction in the completion date is taken as the delay associated with those events. Given the requirement for an as-built program this method is only applicable retrospectively.
The above techniques should be used only after studying the project contract and current construction law protocols.
Conclusion
It should be kept in mind that there is no exact forensic delay method. The output depends on the quality of the data used therein, the accuracy of the assumptions and the availability of verifiable records to back up the delay claim.