Schedule Development & Baselining
Schedule Development & Baselining
Learning Objective
Upon successful completion of this module, you will ;
- Master the steps involved in scheduling
- Understand the significance of critical path
- You will also learn about float, buffer, lag, lead, fast tracking, crashing and their impact on project duration
Effort required – 30 minutes
Lesson Introduction
Upon successful completion of this module, participants will gain good understanding of the steps involved in developing and optimizing project schedules.
Level : Basic
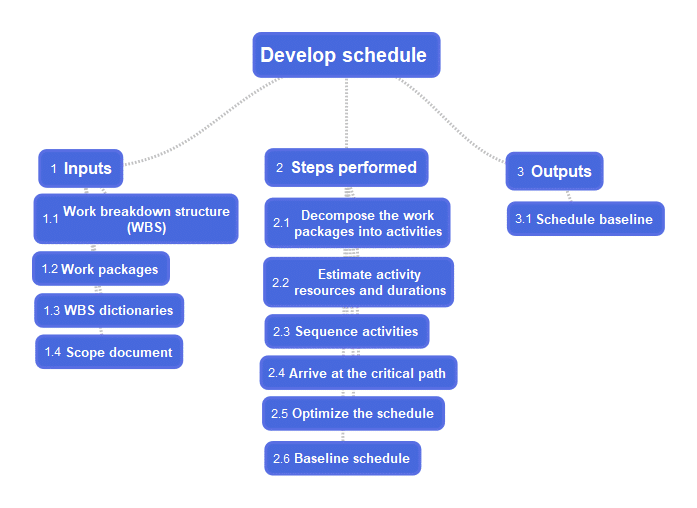
Diagram#1 Develop schedule mind map
- Inputs
- Work breakdown structure (WBS)
- Work packages
- WBS dictionaries
- Scope document
- Steps performed
- Decompose the work packages into activities
- Estimate activity resources and durations
- Sequence activities based on their dependencies
- Arrive at the critical path
- Optimize the schedule by adjusting leads, lags, crashing, fast tracking, resource leveling etc
- Baseline the schedule
- Decompose the work packages into activities

Diagram#2 Scope to Activity decomposition sequence
Every project starts with the high level scope, which gets elaborated into detailed scope. The detailed scope is decomposed into work breakdown structure (WBS). At the lowest level of the WBS are the work packages. The work packages are decomposed further into activities.
- Estimate activity resources and durations
- Analogous estimation – Arriving at the estimate by comparing with a past similar activity
- Parametric estimation – Based on indexes (cost per square feet, time per square feet)
- Sequence activities based on their dependencies
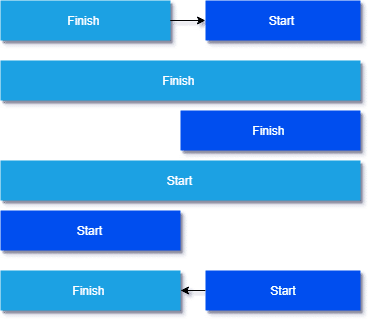
Diagram#3 FS, FF, SS, SF – The four types of activity dependencies
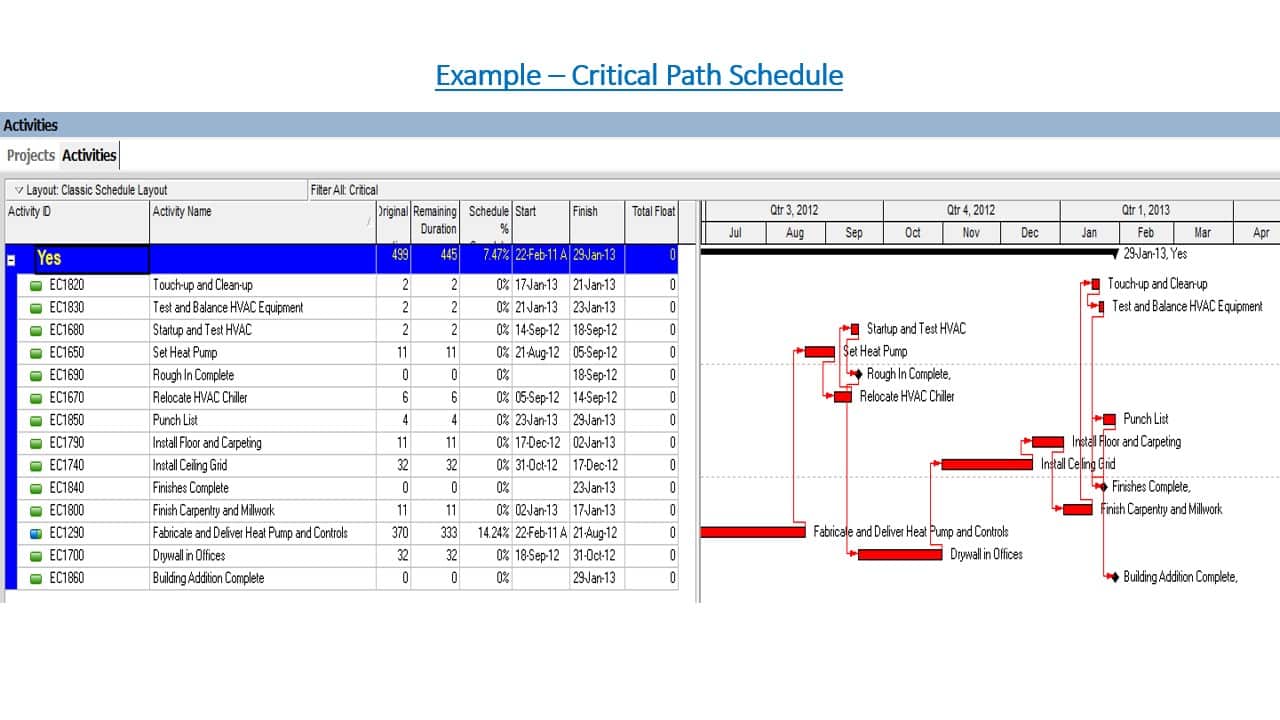
- Arrive at the critical path
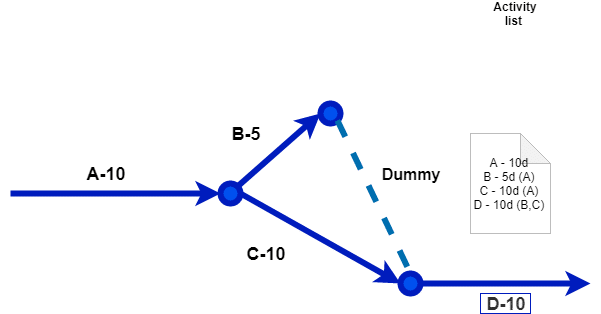
Diagram#4 Activity on arrow diagram
The longest path in the network is the critical path. In the diagram above, the duration of the path A,B,D is 25, and the duration of the path A,C,D is 30, hence A,C,D is the critical path. The activities on the critical path should not slip. If they slip, the project will slip. If any of the activities on the path A,C,D slips by 1 day, the project duration will become 31. Even if there is a delay of 5 days on path A,B,D , the project will not slip.
- Optimize the schedule by adjusting the leads and lags, buffer, float, fast tracking, crashing,resourceleveling
Lag – waiting time between two tasks
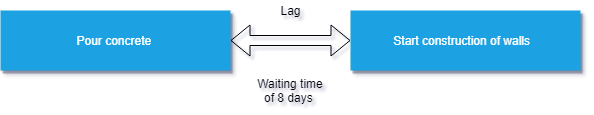
Diagram#5 Lag
Lead – Parallelism between two tasks
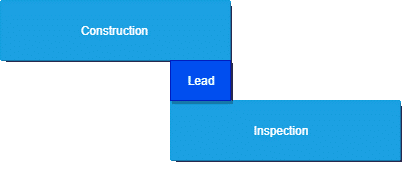
Diagram#6 Lead
Buffer – In projects, one encounter unforeseen contingencies, and we create buffers to deal with them. For example, in the diagram below, if everything goes as per plan, construction can be completed in 3 days time. For dealing with contingencies a buffer of 2 days is added, and the total duration of the task becomes 5.

Diagram#7 Buffer
Float – The amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting the early start date of the subsequent activity. Activities on the critical path will have zero float. An understanding of the amount of float available helps the planner to optimize resource deployment. For example, if a task with very low float is slipping, one can always release resources from a task with lot of float and deploy them in the slipping task.
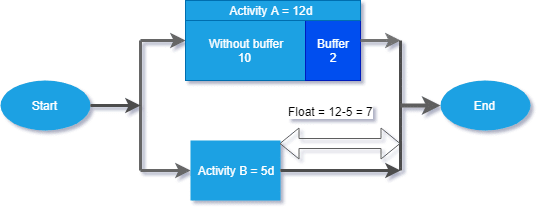
Diagram#8 Float
Resource leveling – When we start allocating resources to tasks, some of the resources can be over loaded, where as some under loaded. The process of optimizing the resource loading against tasks by ensuring that all resources are almost equally loaded is known as resource leveling.
Fast tracking – Trying to do things in parallel, which were originally scheduled sequentially
Crashing – Trying to reduce the duration of a task, by deploying more resources into it.
After the creation of the schedule, we apply all the above mentioned concepts to fit the schedule within the acceptable duration and cost. Once the schedule optimization is completed, the schedule is approved and baselined.
- Baseline the schedule– Version control of the schedule
Outputs
- Schedule baseline